Mass Definition
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, constant and not affected by location. For example, an object's mass is the same on Earth and Mars.
View Lesson on Gravitational Forces Between Objects
Become a member to get full access to our entire library of learning videos, reading material, quiz games, simple DIY activities & more.
Become a member to get full access to our entire library of learning videos, quiz games, & more.
Plans & Pricingto watch this full video.

Access All Videos
and Lessons, No Limits.
Access All Videos

No credit card required,
takes 7 sec to signup.
No card required

Ready-to-go lessons
that save you time.
Ready-to-go lessons
If you are on a school computer or network, ask your tech person to whitelist these URLs:
*.wistia.com, fast.wistia.com, fast.wistia.net, embedwistia-a.akamaihd.net
Sometimes a simple refresh solves this issue. If you need further help, contact us.
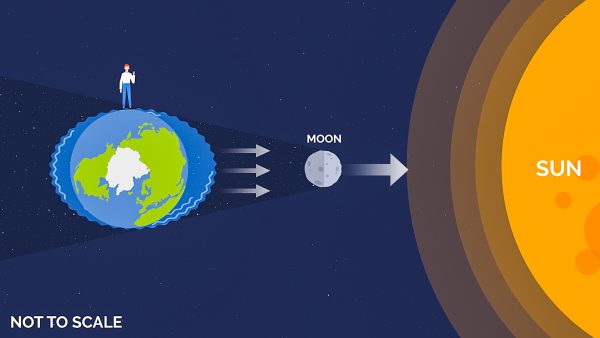
Gravitational Forces Between Objects
Fun Facts
- Mass does not change based on where you are, while weight can vary based on the pull of gravity in that area.
- The force of gravity depends on the mass of an object - the bigger the object, the stronger the force of gravity.
- Mass is measured on a balance, comparing unknown to known amounts of matter.
Why Do We Need To Know About Mass
Learning about mass helps us understand gravity, which is important for many jobs. Astronauts need to know about mass because they work in space where there is no gravity. This helps them move around and stay safe. Construction workers use their knowledge of gravity to make sure buildings are safe and won’t fall over, especially tall ones like skyscrapers.
The way the Moon’s gravity affects the oceans’ tides is related to mass, which is important for people studying the ocean and marine life. People who study space and design spaceships, like astronomers and aerospace engineers, use what they know about mass and gravity to learn more about space and make better spacecraft. Understanding mass is key to many areas, from building and safety to exploring space and the ocean.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out the Full Lesson on Gravitational Forces Between Objects
In this lesson, we learn that:
- Gravity is an attractive force between ANY two objects.
- The force of gravity depends on the mass of the objects and their distance apart.
- This lesson will also explore the difference between mass and weight.
Related Topics
- Absorbency Definition
- Balanced Force Definition
- Binary Code Definition
- Biosphere Definition
- Biotechnology Definition
- Chemical Change Definition
- Chloroplasts Definition
- Climate Definition
- Definition Of Experiment
- Definition Of Science
- Earth’s Rotation Definition
- Electricity Definition
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Definition
- Element Definition
- Environmental Factors Definition
- Frequency Definition
- Greenhouse Gases Definition
- Groundwater Definition
- Habitat Definition
- Humidity Definition
- Internal Structures Definition
- Latitude Definition
- Life Cycle Definition
- Liquid Definition
- Magnetism Definition
- Mass Definition
- Metamorphosis Definition
- Natural Resource Definition
- Ocean Current Definition
- Organ Definition
- Phases Of The Moon Definition
- Predator Definition
- Prevailing Winds Definition
- Reactants Definition
- Renewable Energy Definition
- Respiratory System Definition
- Sediment Filter Definition
- Seed Definition
- Seeing Definition
- Senses Definition
- Tectonic Plates Definition
- Temperature Definition
- Thermal Energy Definition
- Transform Boundary Definition
- Unbalanced Force Definition
- Volcano Definition
- Water Cycle Definition
- Weight Definition


Start a Free Trial Today. Get a $5 Amazon Gift Card!
Teachers! Start a free trial & we'll send your gift card within 1 day. Only cards left. Try it now.
Select Grade
Select Subject
This email is associated with a Science Kit subscription. Kit subscriptions are managed on this separate page: Manage Subscription

-
Download InvoiceScience & Math$/yr
-
Download InvoiceScience Only$/yr

access all lessons
• No credit card required •
"My students loved the videos. I started the video subscription in May and used them as a review before the state test, which I know contributed to 100% of my class passing the state test."
Rhonda Fox 4th Grade Teacher, Ocala, Florida
Use Generation Genius in Your School
Access all lessons free for 30 days.
"My students loved the videos. I started the video subscription in May and used them as a review before the state test, which I know contributed to 100% of my class passing the state test."
Rhonda Fox 4th Grade Teacher, Ocala, Florida
• No credit card required •
Already a member? Sign In
* no credit card required *

* no credit card required *
* no credit card required *

Get District Quote
Discounts start at 3 schools.
Sent!
Thank you for your inquiry.
We will email you a quote as soon as we can.

to Discover the Benefits of Generation Genius
Learn How to Save for Your School & District!
Please login or create an account to access additional resources

no credit card required
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial
-
Unlimited access to our full library
of videos & lessons for grades K-5. -
You won’t be billed unless you keep your
account open past your 14-day free trial. -
You can cancel anytime in 1 click on the
manage account page or by emailing us.
-
Unlimited access to our full library of videos & lessons for grades K-5.
-
You won't be billed unless you keep your account open past 14 days.
-
You can cancel anytime in 1-click on the manage account page.
Cancel anytime in 1-click on the manage account page before the trial ends and you won't be charged.
Otherwise you will pay just $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open.
Cancel anytime on the manage account page in 1-click and you won't be charged.
Otherwise you will pay $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open.
We just sent you a confirmation email. Enjoy!
Done


























































































































 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS