The exponential growth of the human population since the Industrial Revolution has created a negative impact on the natural environment. Increased water consumption and pollution have damaged many ecosystems. Changes to human behaviors such as the types of products we use, conserving water, and the way we live with other species can help reduce our impact on the planet.
To better understand the human impacts on the environment…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Human Population Growth

Modern humans have been around for about 300,000 years. However, around the mid-1700s, the world’s human population grew by about 57% to 700 million people due to the start of the Industrial Revolution. During this time, changes in medicine and living standards resulted in a population explosion. In only 100 years after the onset of the Industrial Revolution, the world population grew by 100% to two billion people. During the 20th century, the world population grew exponentially again, growing to six billion just before the start of the 21st century. That is a 400% population increase in a single century. In the 250 years since the Industrial Revolution, the world population has increased by 6 billion people and is predicted to continue to grow to a total of 8.6 billion by 2030.
Reduce, Recycle, and Reuse

Raw materials from the Earth and energy are needed to create, package, and transport new products to stores and homes. The most effective way to reduce waste is to not create new products in the first place. Reusing products such as clothing, building materials, and storage containers helps reduce the amount of waste produced. Using reusable items such as silverware and glass jars rather than disposable items also helps reduce the amount of waste you produce each day. Recycling is another way to reduce waste. Things like plastic soda bottles can be recycled into clothing and paper can be recycled into new paper products. By following your local guidelines, you can recycle your aluminum, cardboard, glass, paper, and even yard waste to help make a positive impact in your community.
Plastics in Our Environment
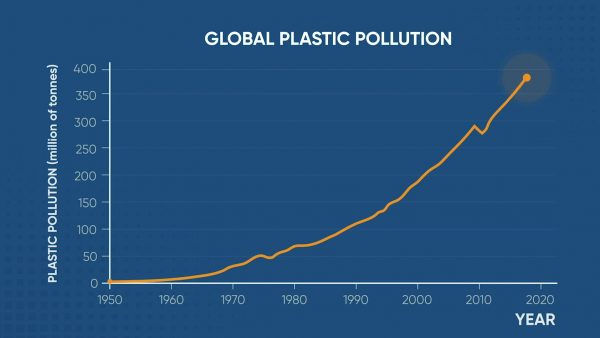
Scientists estimate that more than 8.3 billion tons of plastic has been produced since the 1950s. About 60% of that plastic has ended up in either a landfill or the natural environment. The rate of plastic production has grown faster than that of any other material as we have become addicted to single-use plastic products.
A staggering 8 million tons of plastics end up in the world’s oceans every year. Many rivers carry the plastics to the ocean, which then have a negative impact on our wetland and marine ecosystems. Whether in a river, an ocean, or on land, plastics can remain in the environment for centuries since they are nonbiodegradable. Most plastics never fully disappear, they just get smaller and smaller over time. These tiny plastic particles are swallowed by farm animals or fish who mistake them for food and can find their way onto our dinner plates. If the current trends continue, our oceans could contain more plastic than fish by 2050.
Freshwater Conservation and Production

The U.S. population has doubled over the past 50 years, while our thirst for freshwater has tripled. Freshwater is a natural resource that is anticipated to be in high demand in the near future, with 40 states anticipating water shortages by 2024. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has developed federal requirements mandating water conservation that has produced significant results. Simple changes in human behavior such as turning off the water while you brush your teeth, installing a low-flow showerhead, and watering plants in the early morning or late evening all help to conserve water.
Although freshwater sources are limited, there is plenty of saltwater in our oceans. Desalination is a separation process used to reduce the dissolved salt content in water so that it is suitable for human consumption or irrigation. Ocean water can be desalinated through a process driven by electricity called reverse osmosis or driven by heat called distillation. Unfortunately, both methods are expensive and use a great deal of energy. Currently, there is only about 1% of the world’s population that is dependent on desalinated water to meet daily needs, but this is expected to grow as freshwater becomes scarcer.
Wildlife Conservation

Wildlife conservation is the practice of protecting plant and animal species and their habitats. Wildlife conservation biologists aim to protect plant and animal species as human populations encroach on their natural resources. The goal is to ensure the survival of these species and to educate people on living sustainably with other species. Wildlife preserves are protected areas that are important to maintaining the biodiversity of an area and are also used for scientific study. Conservation biologists have helped protect public lands and write legislation such as the Endangered Species Act of 1973 in the United States to protect various species. They work with law enforcement to prosecute wildlife crimes such as illegal hunting called poaching.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




