A mineral is a natural solid with a characteristic crystal shape. Mineral crystals can form when hot water containing dissolved minerals cools down and forms a solid. Rocks on the other hand are made of mineral pieces mixed together. Rocks are made through the rock cycle! Read more about it below.
To better understand rocks & minerals…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Minerals can form when water within Earth becomes saturated.

Minerals are solids that occur naturally and have a characteristic crystal shape. Hot water deep within Earth flows through cracks, where it can dissolve different substances. When hot water flows toward the surface, it cools and forms crystals. Hot water dissolves more minerals than cold water. When the water becomes saturated (can’t hold any more) with dissolved substances or cools, the water cannot hold onto all the dissolved minerals, and the minerals begin to crystallize on hard surfaces. Examples of minerals that form this way include gold, pyrite, and galena.
Rocks are made of minerals mixed together.

Minerals combine to form rocks. There are three basic types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Within those three rock types are many other subtypes of rocks that are named based on the minerals they are made up of and their crystalline structure. Igneous rocks are formed from hot magma that cools below the surface or lava that cools quickly above the surface. Metamorphic rocks are formed when rocks are exposed to heat, pressure, or both heat and pressure. Metamorphic rocks typically form at plate boundaries and next to intrusions of magma. Sedimentary rocks are formed from weathered bits of rocks (sediments). These sediments are deposited into layers. The weight of overlying layers compact the layers of sediment below, and water flowing through the layers deposits minerals that cement the grains together.
The rock cycle is dynamic.
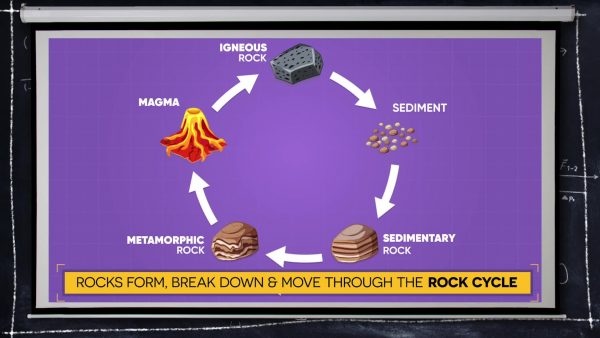
Rocks can change from one type to another through a series of processes known as the rock cycle. There is no one set “path” through the rock cycle. One example of rocks changing from one type to another is as follows: As liquid magma deep within Earth moves closer to the surface, it cools and hardens, forming igneous rock. Over thousands of years, igneous rock breaks apart (weathers), and the bits of rock (sediments) are moved (eroded) by wind, water, ice, and gravity. The sediments form layers; layers near the bottom are compacted by the weight of layers above. Water moving through the layers deposits minerals, which cement the sediments together to form sedimentary rock. These sedimentary rock layers, if exposed to heat and pressure at convergent plate boundaries, are transformed to metamorphic rock. Subducted metamorphic rocks melt as they are pushed deeper into Earth at subduction zones. The melted rock forms magma. The igneous rock formed from cooled magma or lava may follow a completely different path through the rock cycle the next time.
Sedimentary rock has layers called strata.
Metamorphic rocks change forms as a result of heat and pressure.

Metamorphic rocks are sedimentary or igneous rocks that have been changed by high heat and/or pressure. It is not surprising, then, that metamorphic rocks form at convergent and transform plate boundaries. Metamorphic rocks that form in this way have commonly developed a foliated texture (wavy layers). Sedimentary and igneous rocks can also become metamorphic rocks when they come in direct contact with magma below Earth’s surface and hot water (water within Earth heated by magma). This is called contact metamorphism. Metamorphic rocks that form in this way are never foliated.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




