The Earth moves in two different ways. Earth orbits the sun once a year and rotates on its axis once a day. The Earth’s orbit makes a circle around the sun. At the same time the Earth orbits around the sun, it also spins. In science, we call that rotating on its axis. Since the Earth orbits the sun AND rotates on its axis at the same time we experience seasons, day and night, and changing shadows throughout the day.
To better understand Earth’s rotation around the sun….
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Earth’s rotation on its axis occurs every 24 hours.

Earth is always moving. Each day, the Earth makes one complete rotation on its axis. The axis is the imaginary line through the earth that extends from the North Pole to the South Pole.
As Earth rotates, it seems like the sun is moving across the sky, but it’s really the Earth that is spinning. It takes 24 hours to complete one rotation, which is why there are 24 hours in one day.
In other words, if the sun is visible in the morning starting around 6:00 AM, the Earth will spin completely around by the next morning at 6:00 AM and you will see the sun in about the same place.
The Earth orbits around the sun every 365.25 days.
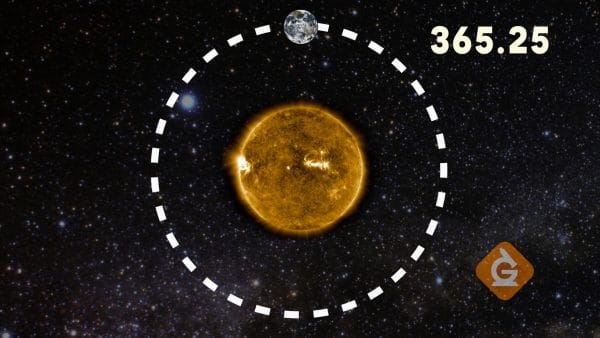
While the Earth is rotating on its axis, it also orbits the sun. It takes a little more than 365 days for the Earth to make a complete trip around the sun.
Other planets have different orbital times. It takes only 87 days for Mercury to orbit the sun, but 12 years for Jupiter to make the journey.
Scientists used to think that the Earth was the center of the universe, but phenomena such as stellar parallax have proven that this is not true because the position of some stars change as we orbit.
Earth's rotation causes observable patterns like night and day.

The light from the sun shines on half of the Earth at any given time. That side is warmer and brighter. The other side of the Earth faces away from the sun (it's dark) so it is cooler and darker. Since the Earth is always spinning, there is a line between day and night and we pass through it each day.
Another pattern caused by the Earth’s rotation is the length of our shadows. Shadows are longer in the afternoon than at noon. If you study shadows and their appearance throughout the day, you can use this information to help estimate the time. Sundials are designed using this idea.
It is important to remember that the sun doesn’t travel across the sky. It looks that way because the Earth is spinning.
Earth’s orbit causes some stars to be visible only in certain months.

Another pattern we can observe due to the earth’s orbit around the sun has to do with constellations. The night sky looks different throughout the year because we can only see in one direction (away from the sun). As the Earth orbits, our view changes. This is why we see different constellations at different times of the year.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




