In ecosystems, organisms compete for the resources they need to survive, grow, and reproduce. Animals compete for air, food, shelter, water, and space. Plants also compete with each other for the resources they need, including air, water, sunlight, and space. These interactions within an ecosystem help keep the populations of various organisms in balance and are necessary to keep an ecosystem healthy.
To better understand the competition in ecosystems…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Environmental factors affect competition for resources.

Competition for resources affects an organism’s ability to survive, grow, and reproduce. For example, the gray fox can live in many places across the United States. However, if resources are limited, the fox’s ability to grow is affected. Plants can be affected in the same way. For example, plants will not reach their full height and width if they do not have enough space to grow.
Genetic factors affect an organism’s ability to survive.

Many genetic factors affect a plant or animal’s ability to survive. Genetic factors include traits that are inherited from parents. Traits can include leg length, which can affect an animal’s ability to run to either catch something to eat or avoid being eaten. Genetic factors also affect things like fur and feather color, which can provide camouflage or attract a mate for reproduction.
Food webs show the transfer of energy and matter within an ecosystem.
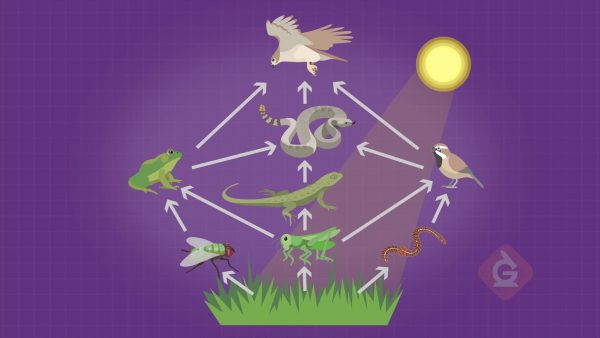
A food web is a model that can be used to show the interactions between living things in an ecosystem. Food webs are used to explain how energy and matter are transferred between various organizational levels. The arrows in a food web indicate where energy and matter are transferred from and what organism receives the energy and matter.
Invasive species can affect ecosystems in many ways.

Invasive species are organisms that are not native to an ecosystem. Invasive species can appear for many different reasons. For example, animals can carry and spread seeds to different areas where they don’t belong because the seeds are on their fur or in their waste. Usually, invasive species are carried to different ecosystems by humans (sometimes accidentally and sometimes on purpose). For example, feral pigs were brought here by early explorers as a source of food but are not common in the southern United States.
There are many careers that study populations.

Many scientists study populations of living things, including wildlife biologists. Wildlife biologists are scientists who make observations and collect data from different populations and population interactions in ecosystems. Wildlife biologists help track populations that may be endangered, and they move animals within ecosystems when an area is becoming overpopulated.
































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









