A chemical reaction is a process in which new substances are formed. The atoms you start with are regrouped into new substances that have different properties. It’s important to remember that the number of atoms before and after a chemical reaction always stays the same.
To better understand chemical reactions…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
When substances undergo chemical reactions, their properties change.

All matter has properties, and those properties can be both observed, and recorded. Properties of matter can also be tested to help determine what the substance is. Examples of these properties are magnetism, flammability, density, and odor. Many other properties of matter exist and by examining a substance’s properties, it can help us predict how it may interact with other substances.
The total number of atoms does not change in a chemical reaction.
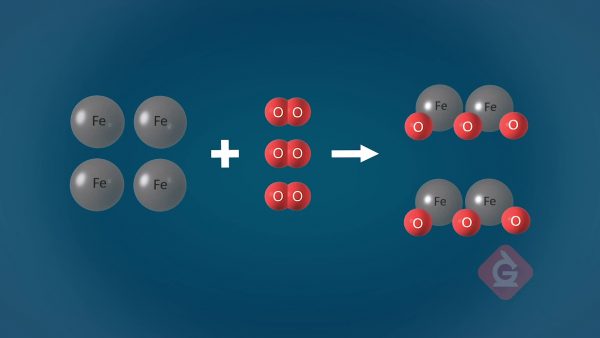
This is commonly known as the Law of Conservation of Matter. Because matter cannot be created or destroyed, atoms can only rearrange themselves in a chemical reaction. For this reason, the final mass after a reaction has taken place will be identical to the initial mass before the reaction took place, even if new substances were formed. Atoms combine to form molecules, and those molecules interact with others differently based on their properties. When molecules interact with each other, they rearrange to form new substances that have different properties than before.
No new substances are formed in physical changes.

Physical changes result in changes of state, or phase changes. They do not result in new substances being formed. Melting and freezing are examples of phase changes. Raising and lowering the temperature of a substance causes molecules to come closer together, forming a solid, or move farther apart, forming a liquid or gas. Many students think dissolving is a physical (or phase) change. However, dissolving results from a chemical reaction taking place in which one substance breaks down, instead of two substances combining to form a new substance. Chemical reactions can also result in new substances when a substance breaks down after adding lots of energy. An example of this is TNT (trinitrotoluene)!
Reactants combine or rearrange to form products.

Because matter cannot be created or destroyed, when atoms rearrange themselves in the presence of a catalyst, new substances are formed called products. These products usually have different properties than the reactants, even though the total amount of mass in the system has been conserved. For example, lighting a gas grill requires the combustion of propane. The chemical reaction looks like this:
C3H8 (propane) + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
There are 10 atoms of oxygen on both sides of the equation, but the oxygen atoms have rearranged themselves combining with hydrogen and carbon to create carbon dioxide and water. The same number of atoms are present before and after the chemical reaction, but new substances have been formed into products.
Many careers use chemical reactions to solve problems.

Chemical engineers and material scientists study chemical reactions to advance space exploration, make medicines, and form new products that solve unique problems. Professional chemists work together with other scientists to combine substances based on their properties. The properties of each substance determines how it interacts with other substances to form new chemicals. Scientists study these properties and the interactions between substances to solve problems and advance the world of science!

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form