We can think of forces as pushes and pulls, and we normally think of one object pushing or pulling another object by touching it. But sometimes an object can push or pull on another one without touching. Forces that can act over a distance like this are explained by fields that can surround an object and exert forces on other objects within that area. Two examples of fields are electric fields and magnetic fields. Although we cannot directly see these fields, we can map them out based on how they affect objects in the field.
To better understand electric and magnetic fields…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Magnetic fields

You know that magnets can attract or repel each other, even without touching. Magnets can do this because they produce magnetic fields that can push or pull other magnets and certain types of metal. Magnets do not attract all metals, but iron, nickel, cobalt, and steel are the most common examples of metals that are attracted by magnets. We can use iron filings to map out magnetic fields. A magnetic field appears as lines that extend from one pole of the magnet and curve around to the other pole. The magnetic fields cause the like poles (north-north or south-south) of two magnets to repel each other and the opposite poles (north-south) to attract each other.
Electric fields
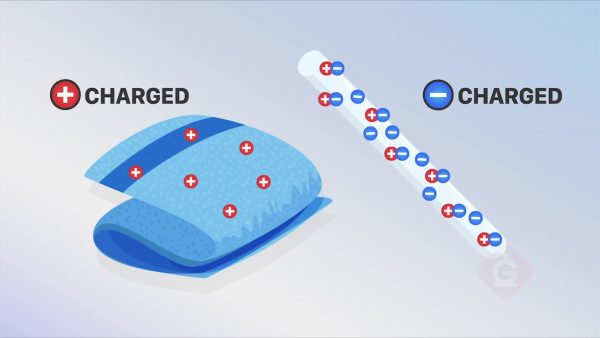
Objects that have a positive or negative electric charge also produce fields. Objects usually become charged by rubbing against each other and transferring negatively charged electrons from one area to another. Similar to magnetic poles, like charges (+/+ or -/-) repel each other and opposite charges (+/-) attract each other. You can detect a magnetic field by observing how it affects a charged object. Electric fields do not have uniform strength. An object with a greater charge will have a stronger field, and the field gets stronger as you get closer to the object.
Strength of magnetic fields

Like electric fields, magnetic fields also get stronger as you get closer to the magnet. A bigger magnet has a stronger magnetic field than a smaller magnet when the two magnets are made of the same material.
Electromagnets

Electromagnets are magnets that can be turned on and off, and the simplest electromagnets can be made by coiling a piece of wire many times. Some electromagnets also have a metal core inside the wire coil. When electric current flows through the coil of wire, it creates a magnetic field. Adding more coils or increasing the amount of electricity flowing through the coil will make the magnetic field stronger.
Real-world applications of electric and magnetic fields

Any device with a speaker, such as a phone or earbuds, relies on magnetic fields to produce sound. Each speaker contains a permanent magnet and a wire coil that becomes an electromagnet when electric current passes through it. The interactions of the permanent magnet and electromagnet cause the speaker to vibrate and produce sound. Laser printers are an example of devices that use electric fields to operate. The toner particles stick to paper because the particles are negatively charged. Once the particles stick to the paper, they are melted into place to form the final image.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









