A wave is a repeating pattern of motion that transfers energy from place to place. When waves come in contact with an object, a few things can happen. The wave can be transmitted, which means to pass through the object. It can be absorbed, in which the wave is converted to thermal energy, or it can be reflected (sent off in a new direction).
To better understand wave reflection, absorption & transmittance…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Waves have properties.

A wave is a repeating pattern of motion that transfers energy from place to place. All waves have properties such as amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. These properties can be used to describe the wave. The amplitude of a wave determines how loud a sound is and how bright light is. Wavelength is the length of one wave. Frequency is how many waves occur in 1 second. The wavelength and frequency of a light wave determine color. A light wave is measured in nanometers. Different wavelengths produce different colors. Higher wavelengths produce brighter colors such as red, and lower wavelengths produce darker colors such as violet.
Sound waves travel through matter.

Sound waves need matter to travel through, but light waves do not. When sound travels through matter, they can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted depending on the waves’ properties. Higher amplitude sound waves are more likely to be transmitted through matter instead of reflected. Lower amplitude sound waves are more likely to be reflected or absorbed, resulting in a lack of an echo. Sound can travel through air, water, and solids. The type of medium sound is traveling through, along with the properties of the sound wave, will determine if it is absorbed, reflected, or transmitted.
Wave absorption.

Waves can be absorbed by matter, depending on what the matter is and the properties of the sound wave. When a wave is absorbed, the matter takes in energy from the wave and, in doing so, lowers the amplitude. For example, when a sound wave hits foam padding, the energy travels through the material and is sometimes converted into heat or other forms of energy. This results in no echo because the sound wave is being absorbed into the material, not reflected. Mechanical engineers use wave absorption measurements when building structures such as music studios and soundproof rooms.
Wave reflection.

Waves are reflected when the density of matter is too high for the wave to pass through or be absorbed. Because of that, the wave is reflected (or bounces off) and then moves in a different direction than it was originally traveling. When sound waves are reflected, there is often an echo because the sound wave is traveling in various directions bouncing off matter. Part of the wave will attempt to pass through the solid, liquid, or gas, but most of the wave will bounce off and travel in a different direction. This will continue until all of the energy in the sound wave is absorbed or dissipates. The process of a sound wave repeatedly reflecting in a space is called reverberation.
Wave transmittance.
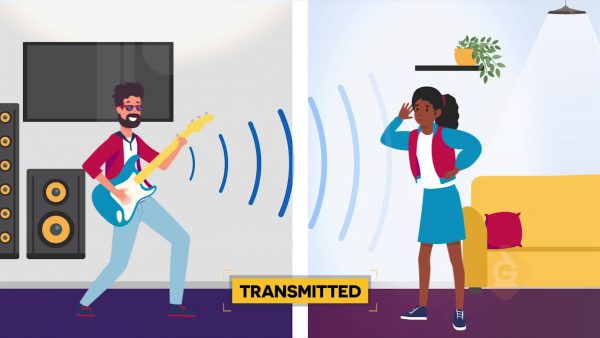
When light moves through liquid, like in a fish tank, it transmits certain colors while absorbing others. For example, when shining white light into the fish tank, you see the color blue because blue light is being transmitted while all other colors are being absorbed. Similarly, when white light hits a leaf, all visible colors are absorbed except green, which is reflected onto your eyes. The colors you see have everything to do with light wave reflection, absorption, and transmittance. Because different colors of light have different wavelengths, some colors are reflected while others are absorbed. This allows different wavelengths of light, and also colors, to be reflected on the human eye, which allows us to see color!

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









