All atoms are made of three smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. The protons and neutrons clump together at the center of an atom and the electrons orbit far away. Atoms can be combined to form molecules through chemical reactions.
To better understand atomic structure…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Atomic Structure
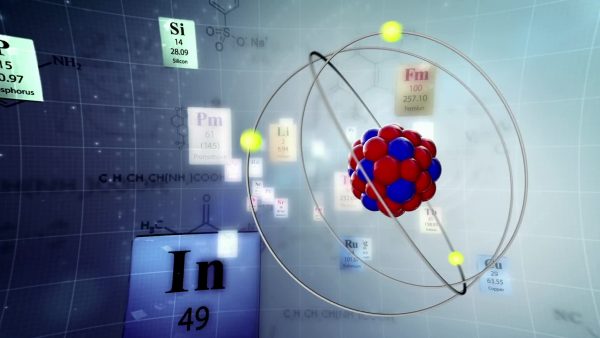
The center of the atom, often referred to as the nucleus, is made up of protons and neutrons. The protons are positively charged, while the neutrons don’t have a charge. Orbiting around the outside of the atom at a tremendous speed and distance are electrons. Electrons are the smallest of the three subatomic particles and have a negative charge. Empty space is found between the atomic nucleus and electrons.
Microscopic Atoms
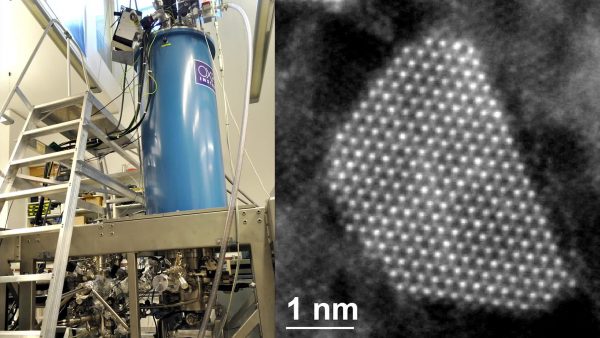
Atoms are extremely small. Atoms are more than 10,000 times smaller than the width of a hair. Even a classroom microscope would not be able to see anything close to the size of an atom. A specialized microscope called a Scanning Tunneling Microscope developed in the 1980s can show us individual atoms. If you were to look at some iron filings with a Scanning Tunneling Microscope, you would be able to see tiny spheres of iron atoms.
Identifying Atoms
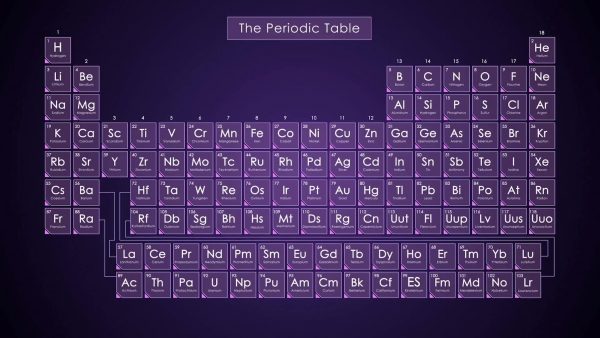
Each element has a certain number of protons, neutrons and electrons. We can find this information by referencing the Periodic Table of Elements. For example, element number 6 on the table is carbon, which is notated by the letter C. The periodic table also shows us that carbon’s atomic number is 6. The atomic number tells us how many protons and electrons are present in the element. From this information we know that carbon has 6 protons and 6 electrons.
Elements and Molecules

Elements can be combined to make molecules. Water for example is H2O. This means that 2 hydrogen atoms are bonded to one oxygen atom. There are endless combinations of atoms that make up all of matter. Some are simple like water, while others are much more complicated such as hemoglobin. A sucrose molecule, what you know as table sugar, is made up of 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen, and 11 atoms of oxygen. Sucrose can be written in a shorthand notation like this: C12H22O11.
Careers in Chemistry

The main field of science that studies atoms and molecules is called chemistry. Chemists use their knowledge of atoms to create molecules that can be used as medicines. In order to make molecules, they need to know which ones react together and which order to react them in. Other types of scientists like biochemists study huge molecules made by nature such as proteins and DNA. The production of insulin molecules to treat diabetes was made possible by the work of biochemists.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









