Anatomy is the branch of science that studies the structures of living things, like their skeletons, organs and muscles. When scientists compare the anatomy of living things to each other we call that, comparative anatomy. It can help us understand how living things are related.
To better understand comparative anatomy…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Human Anatomy
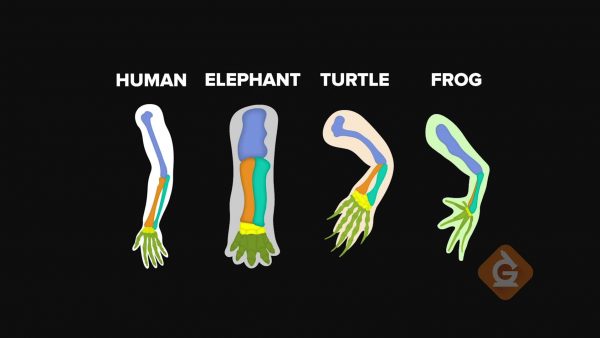
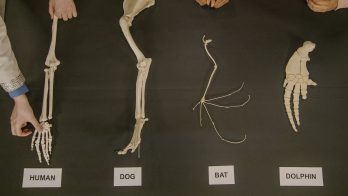
Human anatomy, especially the skeletal system, has many similarities to other organisms. This is evidence for evolution because organisms that share similar structures have common ancestors. The more structures that are similar, the more closely related organisms are in their evolutionary past. For example, a human, a dog, a fruit bat, and a dolphin all have the same pattern of bone structure in the upper extremity—one bone connected to two bones, connected to many bones, connected to finger-like bones.
Development of Embryos
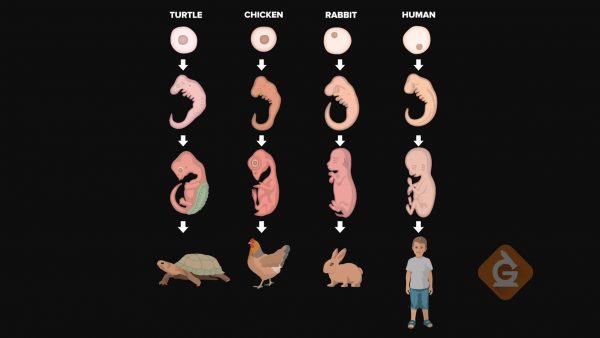
All organisms start from a single cell. Then as those cells divide, a mass of cells form a familiar shape known as an embryo. Embryos are unborn or unhatched babies. Humans develop from embryos like other organisms, and those embryos look similar early in development. In fact, human embryos grow a temporary tail that later disappears. Embryos have similar structures that grow and develop into other structures later in life. For example, pharyngeal slits are present in both fish and human embryos, but they become the gills of fish and the throat and jaw region of a human. Organisms showing similarities in embryonic development are evidence of evolution because the more similar organisms are, the more closely related they are in the past.
The Fossil Record
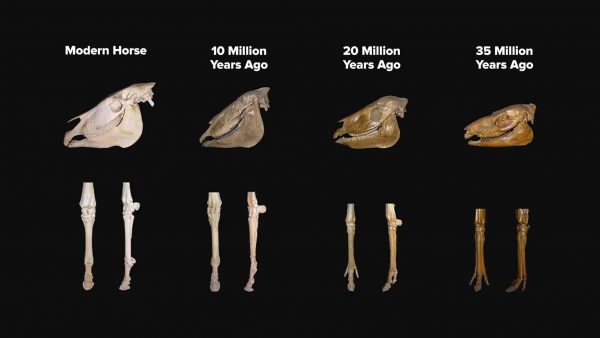
Fossils provide some of the best evidence for evolution and how organisms have changed over long periods of time. Fossils are preserved remains of organisms that once lived but don’t anymore. The entire collection of fossils found is referred to as the fossil record. The fossil record provides evidence for what organisms once existed, how those organisms lived, and how those populations of organisms changed over time. Fossils can be fully preserved in ice and amber or exist as casts, imprints, or molds.
Evolution
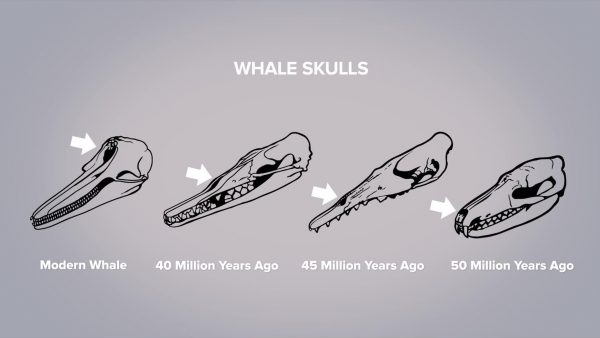
Evolution is the changes in organisms over long periods of time. Organisms possess different types of characteristics that help them live in their environment. For example, whale skulls show how the position of the blow hole has changed over long periods of time. As organisms show small variations in characteristics, certain variations will help them be more successful as their environment changes. So as Earth’s atmosphere and environment have changed, so have living organisms in response. Traits that help organisms to be successful allow those organisms to survive. Organisms that don’t possess those characteristics die. Because the ones with favorable traits survive to reproductive age, they pass those traits on to their offspring, and the traits become more common in populations over long periods of time.
Developmental Biology

Developmental biologists examine and study how organisms develop over time. Specifically, some developmental biologists study human and birth defects. Each year, about 6% of babies born worldwide have some sort of birth defect. That is approximately 8 million children per year. Scientists study embryos of other organisms because of their similar structures to better understand human development without having to destroy human embryos.
































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




