Scientists classify living things based on their shared traits. In addition to identifying each different kind of organism, classification can help us understand how living things are related to each other.
To better understand the classification of living things…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Classification and Groups
When you see an organism that you have never seen before, you probably group it with other, similar organisms without even thinking about it. You use its obvious physical traits to decide what other group it is most like. Although a bat has wings, you wouldn’t classify it as a bird because, in addition to wings, birds have feathers, beaks, and lay eggs—traits that bats do not have. We use shared traits to classify living things into groups.
Dichotomous Key
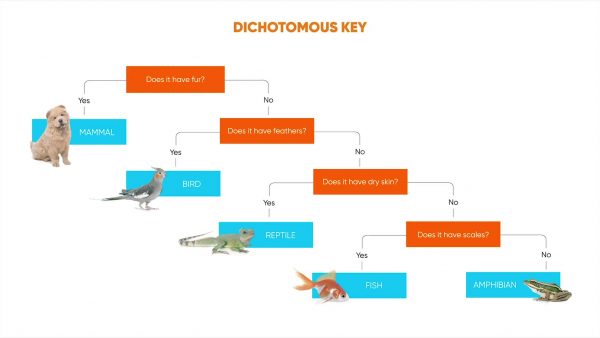
To help identify an unknown organism, you could use a tool called a dichotomous key. Dichotomous means divided into two parts, so the key gives a series of statements consisting of two choices that describe the characteristics of the unidentified organism. You have to choose which of the two statements best describes the unknown organism. Then based on that choice, you move to the next set of statements, ultimately ending in the identity of the unknown. Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways:
1. As a branching flow chart
2. As a series of parallel statements laid out in a numbered sequence
You may use a dichotomous key to classify an animal and determine that it is an amphibian and not a lizard. But trying to determine what kind of amphibian it is requires you to learn about taxonomy.
Taxonomy
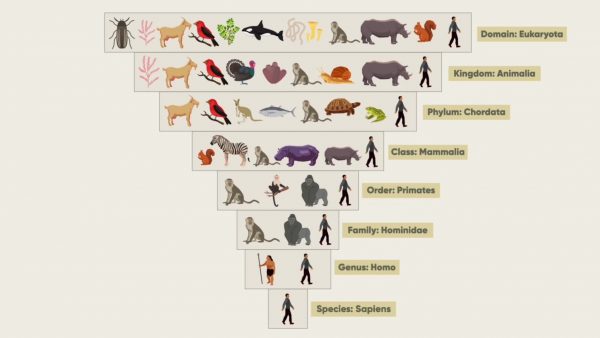
Just like you, scientists group similar organisms together. The science of naming and classifying living things into groups is called taxonomy. Scientists classify living things to organize and make sense of the incredible diversity of life. Classification also helps us understand how living things are related to each other.
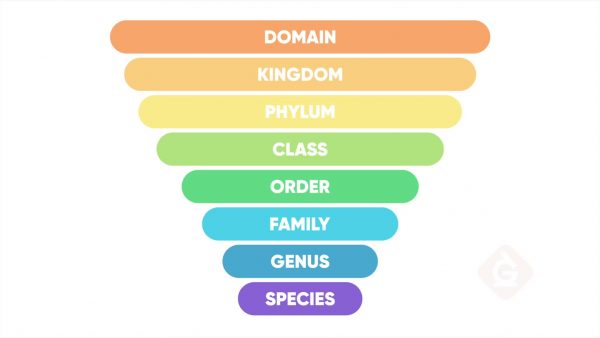
All life can be sorted into three large groups called domains. Kingdoms are the next level and are divided into phyla (phylum, singular). Each phylum is divided into classes, each class into orders, each order into families, and each family into genera (genus, singular). Each genus is divided into one or more species. The species is the narrowest category.
Scientific Names

Every species is given a unique two-word name. Usually written in Latin, it includes the genus name followed by the species name. Both names are always written in italics, and the genus name is capitalized. For example, the human species is named Homo sapiens.
We need scientific names because every language has a different name for the same organism. For example, a cat might be “gato” in Spain and “māo” in China and “goyang-i” in Korea. However, no matter where you live or what language you speak, the scientific name for “cat” is Felis catus. A single, short scientific name for each species avoids a lot of mistakes and confusion.
Classification Using DNA

Taxonomy is not a perfect system. Sometimes you may find two organisms that are visually identical but very different genetically, like a pill bug and a pill millipede. Scientists thought they were the same species until a more advanced method showed them they are NOT!
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule of inheritance found inside the nucleus of cells. DNA is often referred to as the “blueprint of life” because it contains the instructions for making a living organism. Because all living things have DNA, we can compare the DNA of any two organisms to see how similar their DNA codes are. For example, the DNA of Homo sapiens is 99.9% the same as every other Homo sapiens. But as the similarities between different organisms decrease, the similarities in their DNA decrease too. For example, the DNA of Homo sapiens is 96% the same as chimpanzees, 80% the same as cows, and 60% the same as a fly!
Although taxonomy has been used for more than 200 years, it is an ever-changing system. Comparing DNA has made the classification of organisms more precise. As new organisms are discovered that don’t fit into any existing groups, a new group can be created and the system can be updated. It happens all the time!

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




