Every ecosystem is made up of a variety of living and nonliving things. The living things within an ecosystem depend on each other to obtain their energy.
To better understand Food Webs: Cycling of Matter and Flow of Energy…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Producers Make Their Own Food
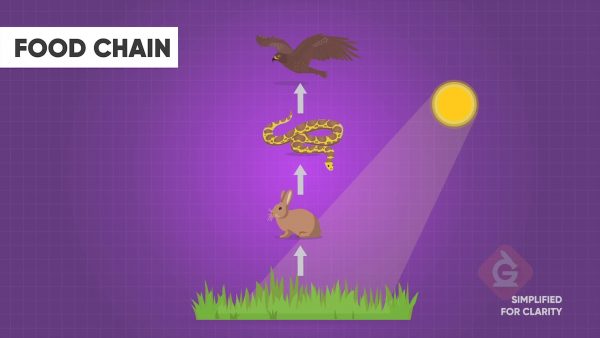
A simple diagram called a food chain represents how energy flows in an ecosystem. A food chain starts with producers. These are the plants at the bottom of the chain. Next, a first order consumer eats the plants to obtain energy. Next in the chain is the second order consumer, followed by a tertiary consumer. Food chains typically have 4 levels, though this can vary.
A food web is the overlapping of food chains within an ecosystem. Living things don’t eat the same thing all the time. Just like people, animals like variety in their diets. This results from living things eating from multiple food chains, which creates a food web. Some living things may eat from different levels of a food chain. Bears for example, consume plants, but also consume fish.
Ecosystems Rely on Chemical Processes

Living things undergo chemical processes that are essential to the living things in an ecosystem. Plants are the producers of an ecosystem and they undergo a process called photosynthesis to make food. This chemical process uses energy from the sun to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen. Likewise, when animals take in food, their bodies undergo a process called cellular respiration. This chemical process takes sugar and oxygen and forms carbon dioxide and water while releasing energy.
Energy Flows Through an Ecosystem

All ecosystems start with energy from the sun. Without sunlight, plants cannot undergo the process of photosynthesis. Using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide, plants make sugar and release oxygen. When a consumer comes along and eats the plant, it gains some energy from these sugars. When the next consumer in the food chain eats the first consumer, energy is passed from one consumer to the next. Since the amount of energy decreases with each level of the food chain, ecosystems can only support smaller numbers of consumers as you go up the food chain. At the top of a food chain, there might only be one hawk. At the bottom of the food chain, there would be many plants.
Decomposers Play an Important Role in an Ecosystem

Decomposers are organisms such as worms or maggots, that break down dead matter. This is important to the cycling of matter in an ecosystem. As the decomposers feed on dead animals and plants, they break down the molecules into carbon dioxide and water molecules that go back into the soil. The amount of matter in an ecosystem never changes; it just cycles through the ecosystem in different ways.
Many Careers Study Food Chains

Several different careers study food chains. Marine biologists study food chains within the ocean ecosystem. This is important to humans since humans consume food from the ocean ecosystem. Through their studies, marine biologists have learned that the chemical mercury can be passed from smaller fish to larger fish. This impacts our food supply and could be harmful if too much of certain types of fish are consumed.
Another career that studies food chains is a registered dietician. A registered dietician helps people make meal plans that work for them. Some people have food allergies or other dietary needs that require the help of a registered dietician. Registered dieticians also work with schools to design healthy food programs for growing students.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









