Plants and animals rely on their various components to work together in order to maintain health and survive. Different multicellular organisms are made of different systems, but all systems are organized in the same way. Living systems are interdependent. One system not functioning normally will affect the other systems in some way.
To better understand Multicellular Organisms…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Systematic Origination
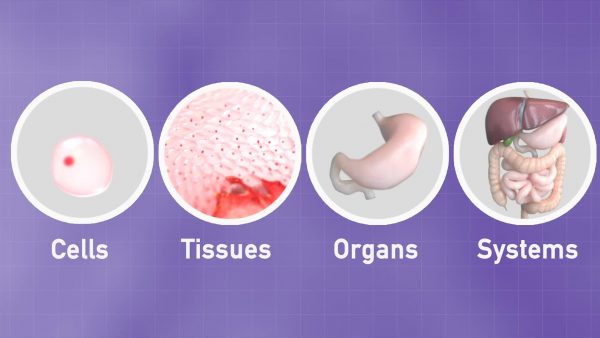
Whether you are investigating a plant or animal system, multicellular organisms are all organized the same way. Body systems can be broken down into components called organs, organs are made of different kinds of tissue, and tissue is made from groups of specialized cells.
Animal Systems
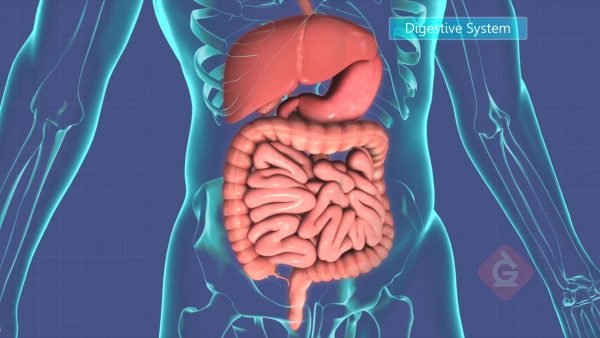
Animals rely on several different systems to survive. These systems work together to allow blood to flow, eat and digest food, and move around. Some of the major systems in animals are nervous, digestive, circulatory, respiratory, excretory, muscular, and skeletal. But some animals, like humans, also have other smaller systems that help them too.
Plant System
Plants rely on systems to survive. These systems work together to allow the plant to make food, to allow water to travel throughout the plant, and to help the plant reproduce. Plants also have organs such as roots, stems, and leaves. But unlike animals, plants have only two major systems: the root system and the shoot system.
System Interdependence
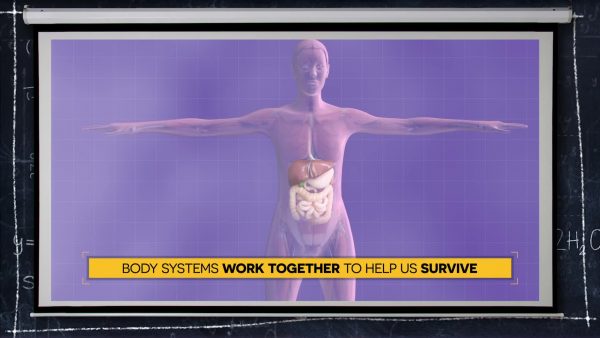
Systems depend on each other to function normally. For example, the respiratory system brings oxygen into the body, and the circulatory system moves oxygen throughout the body. When systems work together like they should, plants and animals are able to grow and reproduce. If one system is not functioning normally, it can affect other systems. For example, wearing a cast to heal a broken bone will affect how you can use your muscles.
Doctors Who Specialize in Treating Body Systems

Doctors who focus on figuring out and treating a single system are called specialists. For example, a neurologist studies the nervous system, and a gastroenterologist focuses on the digestive system. The medical field has many specialized disciplines. There are even doctors who study only special parts of certain systems, such as hematologists who study the cause, treatment, and prevention of diseases that are related to blood.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form







 GENERATION GENIUS
GENERATION GENIUS




