To understand how plants and animals interact, scientists make diagrams called food chains. A food chain shows a sequence of living things in which one organism eats the one below it. Most animals eat more than one thing, so to show ALL the feeding relationships, we use food webs which are made of many intersecting food chains.
To better understand the food web definition….
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Energy in food can be traced back to the sun.

Living things need a constant supply of energy. The sun provides that energy, which is transformed into food by plants through photosynthesis.
Herbivores (plant-eating animals) eat the plants and receive energy. When the herbivore is eaten by a carnivore (an animal that eats herbivores), the energy from the herbivore is transferred to the carnivore. The transfer of energy from one organism to another makes up a food chain.
Animals eat to get energy and building blocks.
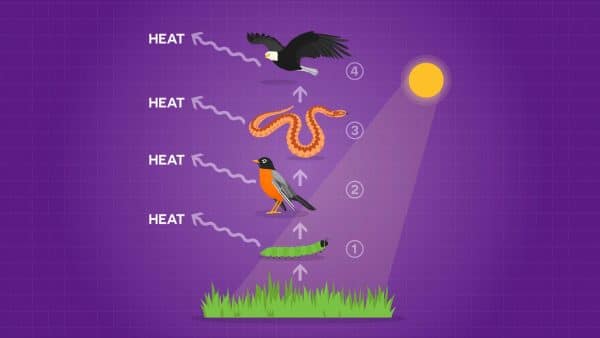
All living things need food to provide materials for growth. Food chains start with organisms that make their own food, called producers. Plants are the most common producers. Animals are called consumers because they do not make their own food -- they eat, or consume, other organisms.
A food chain typically only has a few steps (usually 4 at the most). This is because each time one organism eats another, some of that energy is used up and released as heat.
In fact, you are releasing heat energy right now as you read this because your body is burning food to keep warm! Since some energy gets used up in each step of the food chain, there can only be a few steps, otherwise there is not enough energy left for the organism at the top.
A food web is a model of intersecting food chains.
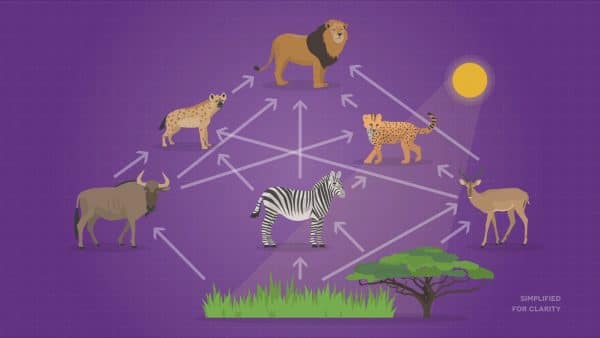
Most organisms can eat, and be eaten, by many different animals. A food chain wouldn't be able to show this. Food webs show all these connections. They are more complicated but more accurate.
In the African savannah food web shown here, we can see multiple arrows pointing to different animals. The arrows show the direction the energy is transferred. For example, we can see that zebras eat trees and grasses, so arrows from trees and grasses are pointing to a zebra.
The arrows pointing from the zebra to cheetahs, hyenas, and lions tell us that the zebra is eaten by these animals.
The lions are at the top of the food web, which means they are not eaten by any other type of animal (except by decomposers when it dies). We call this an apex predator.
Decomposers break down dead organisms.

One group of consumers that are often not shown in food webs are decomposers. Decomposers are organisms (mostly bacteria and fungi) that break down dead plants and animals, eventually turning them into nutrients that will be added to the soil.
These nutrients are very important to continue the cycle in the ecosystem. Slugs, earthworms, millipedes, and centipedes also help break down dead things. Without decomposers, nutrients would not get recycled and we would have dead material piled up everywhere.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









