The four divisions of the year (spring, summer, fall and winter) are marked by weather patterns and hours of daylight in a particular region. These patterns are a result of Earth’s 23.5° tilt of axis and its changing position as it orbits the Sun.
To better understand the causes of seasons…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
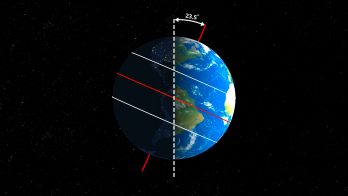
Earth’s Tilt of Axis
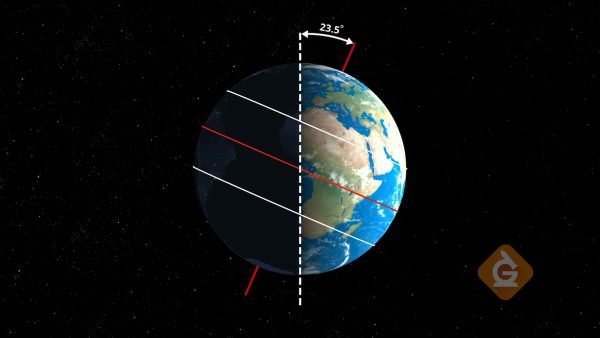
Earth spins around its axis once every 24 hours. The axis is an imaginary line on which Earth rotates. This imaginary line intersects the surface of Earth at the North Pole and South Pole. As Earth orbits around the Sun, it spins on its axis, which is tilted 23.5° relative to the plane of its orbit. Earth’s tilt of the axis points in the same direction in space but changes its position relative to the Sun depending on where it is located during its path of orbit.
During the month of June, the Northern Hemisphere and North Pole point toward the Sun. This causes temperature increases and changes in the atmosphere in the Northern Hemisphere that indicate the season of summer. During the month of December, the Southern hemisphere and South Pole point toward the Sun. This causes temperature increases and changes in the atmosphere in the Southern Hemisphere that indicate the season of summer.
Light Intensity
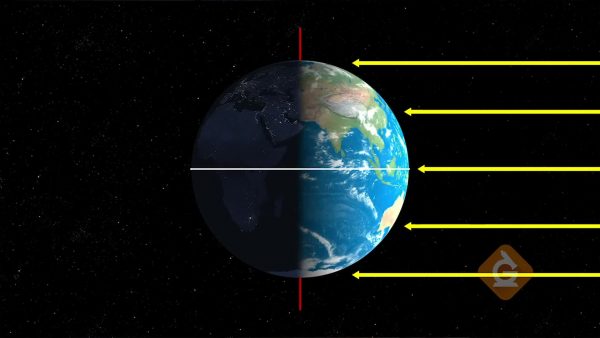
Light is a form of energy that can travel through space. Light energy can be seen by the human eye and is given off by things such as stars, light bulbs, lasers, and hot objects. Light energy is also used by plants to produce food through the process of photosynthesis. When there is more light energy, plants are able to produce more food, which helps them grow.
Light can be measured to determine its intensity or how much energy is hitting a surface. Light travels in a straight line until it hits something else that may block or reflect the light in a different direction. When light travels in a straight line from the Sun to Earth and hits the surface at a 90° angle, it is the most intense and transfers the most energy. This energy is known as solar radiation. When light hits the surface of Earth at a smaller angle, less energy and solar radiation is transferred because the light is spread out over a larger area of Earth’s surface.
Latitude
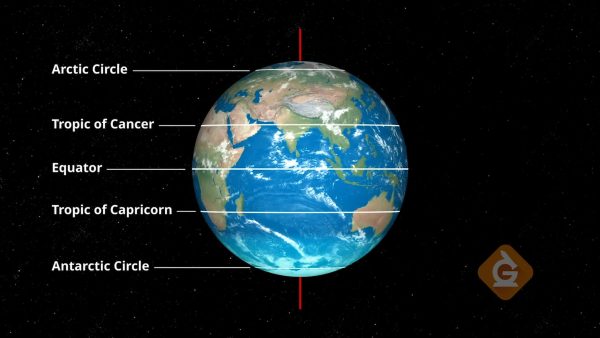
Latitude are imaginary lines that run east and west to measure the distance north or south of the equator. The equator is a line of latitude that divides Earth into two equal hemispheres and is located at 0°. The angle between the North Pole and the equator is 90° and forms a right angle, thus creating the latitude of 90°N (north). The same is true for the South Pole, which creates a latitude of 90°S (south). The latitude of any particular location on earth is measured by the degrees of the angle between that location and the equator. The farther away from the equator, the greater the latitude will be.
There are four lines of latitude other than the equator. These lines have special names and are marked on most globes to create regions with similar conditions during the seasons. The Arctic Circle and Antarctic Circle are the most north and south of these latitudes, with the Arctic Circle found at 66.5°N and the Antarctic Circle found at 66.5°S. The areas between these circles and the North and South Poles are where you can find the coldest temperatures and most extreme differences between the seasons. The Tropic of Cancer can be found at 23.5°N between the equator and the Arctic Circle, and the Tropic of Capricorn can be found at 23.5°S between the equator and the Antarctic Circle.
Daylight Hours
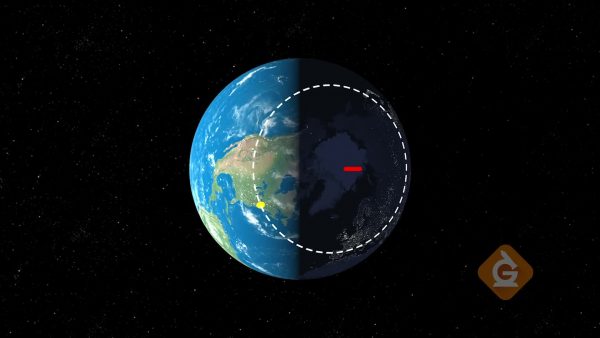
The number of hours of daylight changes for a location depending on the season and the latitude. At the equator, the number of hours of daylight remains close to 12 hours in all seasons of the year. However, for locations above and below the equator, the summer has the most hours of daylight and the winter has the least hours of daylight. The more north or south you travel, the larger the difference in daylight hours between the summer and winter. The North Pole is an example of the extreme difference in daylight hours between the summer and winter. At the peak of summer, there are 24 hours of daylight; at the peak of winter, there are 0 hours of daylight.
Planetary Astronomer

Many types of scientists study space, and they are called astronomers. They study the Sun, Moon, stars, planets, and other celestial bodies in the universe. A planetary astronomer studies planets, including how seasons might occur on other planets. Planetary astronomers have found that Mercury, the planet closest to our Sun, has no tilt as it spins on its axis. The lack of a tilt of axis causes no seasons on Mercury. However, because Mercury does not orbit the Sun in a perfect circle, there are times when Mercury is closer to the Sun (causing Mercury to become warmer) and farther away from the Sun (causing Mercury to become colder). Planetary astronomers have found that Earth travels in close to a perfect circle as it orbits the Sun, so the seasonal temperature variations are not caused by Earth’s orbit but by the tilt of Earth’s axis.
Planetary astronomers have also found seasons on other planets in our solar system. Venus, the second planet from the Sun, has a tilted axis of only 3°. Because the tilt is so small, Venus barely experiences any temperature changes as it orbits the Sun. Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, has a tilt of axis of 25°. This tilt causes all four seasons on Mars, but the seasons are much longer than those on Earth because Mars takes twice as long to orbit the Sun.
































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









