Biodiversity describes the variety of living things within a single ecosystem. This includes numbers and diversity of species. The biodiversity found within an ecosystem can help determine its health. For an ecosystem to maintain diversity, it has to have balance among the organisms living there.
To better understand maintaining biodiversity…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Ecosystems

In ecosystems, organisms compete for the resources they need in order to survive, grow, and reproduce. Animals compete for air, food, shelter, water, and space. Plants also compete with each other for the resources they need, including air, water, sunlight, and space. These interactions within the ecosystem help keep the populations of different organisms in balance and are necessary to keep an ecosystem healthy.
Food webs show the transfer of energy and matter within an ecosystem.
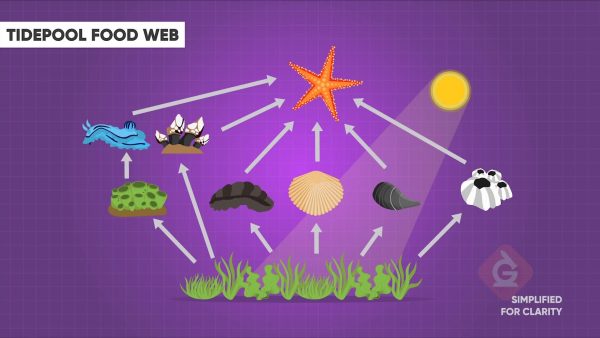
A food web is a model that can be used to show the interactions between living things in an ecosystem. Food webs are used to explain how energy and matter are transferred between the different organizational levels. The arrows in a food web indicate where energy and matter are transferred from and what organism receives the energy and matter.
Ecosystems have keystone species.

In ecosystems, some species have a more important role in keeping the system in balance. These are keystone species. Each ecosystem has its own keystone species. For example, the keystone species in the tide pool was the sea star; however, the sea otter is the keystone species in the nearshore kelp forests.
National parks help protect biodiversity.

President Woodrow Wilson established the U.S. National Park Service in 1916. Currently, the National Park Service maintains 419 national parks that cover more than 84 million acres, including land in Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and Guam. The system was set up to protect native plants and animals that live within those ecosystems.
Careers in Science: Conservation Biologist

A conservation biologist is scientist who studies how humans impact ecosystems. They study the biodiversity within ecosystems by gathering data on the different populations to determine ecosystem health. If the ecosystem has a problem, a conservation biologist can help develop a solution so that biodiversity and ecosystem health are maintained.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form