Convex mirrors allow us to see a wider view. This can help drivers see oncoming cars and drive more safely.
There are many sources of light.

Sources of light can be divided into two groups: natural and made by humans. The sun is the most important natural source of light. The sun allows us to see during the day. Stars and lava from volcanoes also produce their own light. Some animals can produce their own light, such as fireflies and some glowing jellyfish.
Humans have created other sources of light. Light bulbs help us see in dark areas. Before light bulbs were invented, people used candles to provide light.
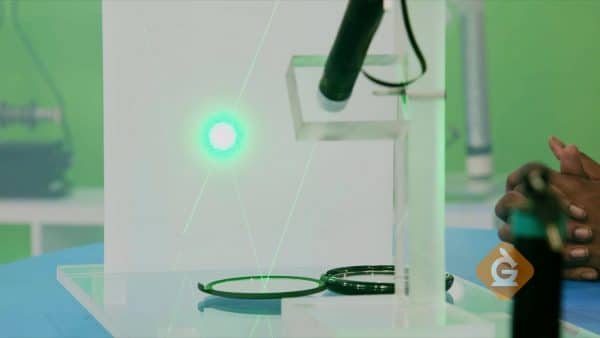
Laser beams are another source of light. Some high-powered laser beams can cause chemicals to explode!