
Genes are sections of genetic material that determine the traits of a living thing. Mutations are changes in those genes which can cause traits to change. Some mutations are beneficial, some harmful, and others have no effect.
To better understand genes & mutations…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Deoxyribonucleic Acid

Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is genetic material found in the cells of all living organisms. DNA contains the code of life and is unique to each organism. DNA is passed from parent to offspring through both asexual and sexual reproduction.
Mutation

Mutations are changes that occur in our genetic material. Changes can occur at any time during an organism’s life span. Mutations can be inherited or happen randomly during cell division or be caused by environmental factors, for example, too much Sun exposure.
Chromosomes
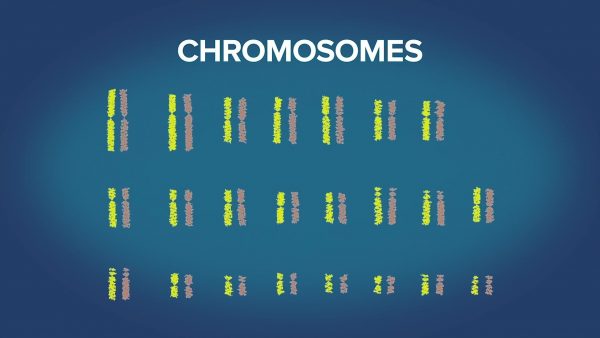
Chromosomes are tightly coiled strands of DNA and are found in the cells of living things. All organisms have a specific number of chromosomes, for example, humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs). All living things get their chromosomes from their parents. In asexual reproduction, all the chromosomes come from a single parent, and in sexual reproduction each parent contributes equal amounts. In humans, an offspring inherits 23 chromosomes from mom and 23 from dad.
Careers in Science: Forensic Scientist

Forensic science uses biology and chemistry to collect and analyze evidence from crime scenes. Forensic scientists work in the field and are experts in evidence collection, which is important, so the evidence does not get contaminated. They also work in the lab, where they take the evidence and analyze it to help solve the crime.
Careers in Science: Virologist
A virologist studies viruses. Viruses are microscopic particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses are nonliving particles that can infect plants, animals, and even bacteria. Viruses are different from bacteria because bacteria are living and can reproduce on their own; however, viruses cannot reproduce on their own and need a host cell to reproduce.
GENES & MUTATIONS VOCABULARY
GENES & MUTATIONS DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
What is DNA and why is it important?
What are chromosomes and what do they do?
What are genes and how do we get them?
How are proteins made and what do they do?
Explain how a mutation can happen and give an example.
Give an example of a mutation and explain if the mutation is good, bad, or doesn’t change the organism.
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial





